–

S.Sivathasan
What is the above subject? Appellation of a Seminar.
Held at: Marga Institute, Colombo.
Held on: May 16th, 2013
Occasion: To launch a publication
Produced by: Independent Diaspora Analysis Group (IDAG)
“GAME FOR THE CHILD, AGONY FOR THE MOUSE”.
So runs a Tamil proverb highlighting the point that an event can be both a pastime and a tragedy at the same time. Making a game of numbers massacred is appalling. Even if the purpose be a call to the adversary not to inflate the figures, it is equally defiling. The choice of the wrong word is prejudicial to the analysis, casting misgivings about detached study or objective conclusions.
A Report on the seminar appears in Ground Views of May 29th. It was said at the seminar that “citing large and inaccurate figures raised issues… Continued recycling of spurious figures can only inhibit the healing process”. Soon after the war some of us computed the likely figures of those entrapped in the final stages of the war. We based it on the census figures of 1981 for the Wanni, subsequent official estimates by the Department of Census and Statistics, extrapolation based on national magnitudes, estimate of internal migration and guesstimate of emigration from the Wanni. Also reckoned alongside were statistics of Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs) and official figures of refugee assistance recipients with which we were conversant. My position as Secretary Rehabilitation in the North East Provincial Council and immediately subsequently as Advisor in the Central Ministry of Rehabilitation, gave me access to such information.
For those encircled, rendered displaced and then confined to camps, we arrived at the figure of 300,000 plus. Why not 350, 000 or 400,000? If we were erring, we preferred to be on the conservative side. What did the government say and later trumpet Goebbels style repetitively? 70,000. When evidence overwhelmed, the figure of 300,000 was announced by the government in acknowledgement. Why were small and inaccurate figures given in the first instance? Why a predilection for the spurious? To serve two purposes. The government knowing full well its cavalier treatment of food and medical needs of the encamped refugees, had the necessity to show particularly the international community that the fraction of less than a fourth it sent met the needs adequately. Secondly, to pull wool over the eyes of everybody by suggesting that a residue of 70,000 couldn’t have generated 40,000 casualties.
Which approximation is credible and which is a strain on credibility? 300,000+ refugees and 40,000+ casualties or 70,000 refugees announced by the government and about 8,000 casualties proclaimed by its apologists? In contrast was our experience with the UNP government’s avowed policy of keeping the people fed in the war years of the eighties. Data from District Administration were accepted about food needs of both civilians and refugees and the requirement was met. This was despite severe interruptions to road and rail transport.
Mr.MDD Peiris as Secretary Food in the eighties, undertook a heavy responsibility upon himself in organizing sea transport and even authorizing high freight rates when the situation demanded. Once he told me “Whatever may be happening in the country, we have to keep the people fed”. With such an attitude which reflected the government’s as well, he made a difference. No attempt was made to reduce the quantities and then to play the numbers game adroitly. Tamils know that conditions were exceedingly easy in 2009 to transport by road and distribute food, medical supplies and refugee requisites in the Wanni, compared to endemic disruptions in the eighties.
Numbers do matter it was said. True. They express the truth and make an impression when underlain by credibility. Transparency is the fount for credibility and a clear exposition of the methodology employed
Is the anchor of such transparency. But we do not see it when one number is transposed for the other. Instead a dazzling display is made of the competence of the weaver and the tailor. Unfazed by the marvel of the Emperor’s Clothes, Tamils reach for international investigation. It is their perception that whatever be the competence of this Sri Lankan Diaspora membership, the credentials of a truly international team will inspire more “confidence in its impartiality and competence”.
One may also ask whether the Department Of Census and Statistics cannot do a good job of it. Another may respond why not? I seek a clarification from the Department regarding the total strength of the diaspora population. My computation is as follows:
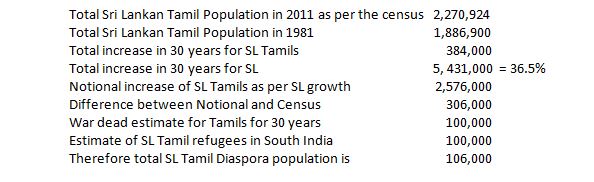
Does it appear rational to place the total diaspora population in Europe, Canada, US and Australia at 100,000? Is there trust in a product of indigenous effort when there is such a variance between popular perception and a governmental source? DCS can clarify if my computation is wrong. The insistent demand for impartial international investigation may be better appreciated in this background.
The expression “spurious figures” is double edged when opposing parties engage in recycling. When 40,000 is inflated to 80,000 does it become a half truth? If 8,000 is deflated to 4,000 it doesn’t become doubly true? Truth alone triumphs and inspires credibility. That’s why all eggs are placed in the international basket by the resident Tamils and the diaspora. If the purity of the government is lily white, why should it hesitate to have the air cleared? If the haze remains, 8,000 will continue to be called spurious.
It was said at the seminar that spurious figures continually recycled can only inhibit the healing process. It doesn’t follow however that exact figures will promote the process of healing. The process would demand a change of disposition with initiatives coming from the government on policy and programme. As of now it is reconciliation on paper and alienation on ground.
If we look at Irish-British relations, only estrangement could have resulted from the way the British treated the Irish. In the 16th & 17th centuries vast multitudes were massacred by the British in Ireland. Close on it, with the army in brutal collaboration, Irish were dispossessed of swathes of territory. This land expropriated from Irish Catholics was given to British Protestants. Is what is happening in Sri Lanka any different? Will it not inhibit the healing process? Oliver Cromwell’s massacres in the seventeenth century, complemented the earlier ones. Need anyone be surprised that Jonathan Swift an eminent Irishman, author of a few books including Gulliver’s Travels, said “Burn everything British but their coal”. These produced the brilliant rebel Robert Emmet, who was executed by the British in 1803. When he was sentenced he made a memorable speech in which he said “My lamp of life is nearly extinguished”. How many lives were so extinguished since 1956 to now in SL with no recompense or show of remorse? Did the healing process ever commence?
Irreconcilability produced an independent Ireland which left the Commonwealth in 1949. Was it obduracy? No. Was Mountbatten killed for love of carnage? No. How did they renounce terrorism? Their economic lift off commenced in 1987. In North SL the the drive is towards the pastoral age. In Ireland their wealth level, disposition, approaches and relationship changed. In Ireland the per capita GDP in 2012 was $ 41,921 and UK’s $ 36,941. Net immigration has overtaken net emigration. A people long oppressed have surged ahead of the oppressor.
War without witnesses is only a contrived description to make satellite images appear to be the sole information source. Over 300,000 herded into Mullivaaikaal are witnesses. Was an effort ever made to record evidence from a sizeable number without army presence anywhere round? Was any evidence examined for corroboration and analysed to establish credibility. Aren’t four years enough to count the dead and the injured with information from those who suffered loss? Has governmental or social responsibility or interest in them ever been evinced? Instead satellite images of shell fire and their interpretation are relied on as the sheet anchor of circumstantial or corroborative evidence. All these for a ‘humanitarian operation’ by the SLA, the very force that is under a cloud. Was gun fire only with rubber bullets? With no effort at healing, will the process be accomplished? Mao Tse Tung asked “With Platonic Love can you bring forth a child”?
What the Tamils seek is that truth be discerned. For this international investigation is needed as the single means to ferret it out.


















